On April 26, 2011, Nippon Electric Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. announced the development of a new positive electrode composite material based on lithium iron phosphate LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate) material, which reduces the resistance of lithium iron phosphate material and extends the lithium ion rechargeable battery. life span.
This material is the result of a collaboration between the Electrochemical Industry Co., Ltd. and the SEI Group in Tsu City, Mie Prefecture, Japan, which focuses on the research and development of lithium-ion rechargeable battery materials.
At present, a large proportion of lithium ion rechargeable batteries use lithium iron phosphate LiFePO4 as a positive electrode material. This material has many advantages. First, the energy density is higher, the theoretical specific capacity reaches 170 mAh/g, and the actual specific capacity can reach 140 mAh/g (0.2C, 25 °C). Secondly, it is safe. Lithium iron phosphate does not contain heavy metal elements harmful to human body. It is the most safe lithium ion battery cathode material. The third is no memory effect, avoiding crystallization like nickel batteries. The fourth is that the charging speed is faster.
The effect of lithium iron phosphate cathode material on battery life is divided into two. The material has high lattice stability, the lattice is rarely affected by the intercalation and extraction of lithium ions, and the reversibility is good. Under 100% DOD, it can be charged and discharged more than 2000 times; but the lithium iron phosphate electrode material The electron ion conductivity is relatively low, and the life is still affected under the charging-discharging operation with a large current intensity.
According to the Electric Chemical Industry Co., Ltd., for automotive applications, the total number of charge-discharge life cycles of batteries using lithium iron phosphate electrode materials can be improved. If a new material developed on the basis of lithium iron phosphate is used, the total charge-discharge life cycle of the battery can reach or exceed the level of other non-ferrous based cathode material batteries.
The Electric Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. added acetylene black and carbon nanofibers as conductive modification components to lithium iron phosphate. Acetylene carbon black is mainly produced by Acetylene by Pyrolytically Decomposing. The three materials are cured after mixing, so the conductive path can be arranged according to the established target, thereby reducing the resistance characteristics. The resistivity of the new material is reduced by about 30% compared to existing iron-based cathode materials.
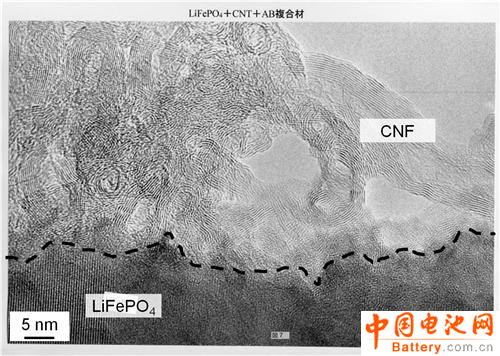
Fig. 1 is an observation image of a novel positive electrode material under a transmission electron microscope (Transmission Electron Microscope). The dotted distribution area is lithium iron phosphate; the carbon nanofibers are distributed above the lines in the figure. Since the carbon fibers overlap each other (Lap Over), the appearance tends to be concentrated. Acetylene carbon black is not shown on the graph because it is too small and adheres to the carbon nanofibers.
The processing details of the manufacturing process were developed exclusively by the company and have not yet been announced. However, compared with the existing iron-based cathode materials, the new materials do not need to be pulverized during processing. In addition, the processing procedure does not require the addition of special equipment, so the cost increase is not obvious.
After the resistivity decreases, factors such as waste heat affecting the working life of the battery are suppressed to a certain extent, so that the working life of the iron-based cathode material can be comparable or even exceeded with other cathode materials, such as Manganese-based materials and ternary composites. A positive electrode material such as copper (tin-tin-bismuth, Cu-Sn-Sb).
At the end of the life of the battery, the battery may be reduced by as much as 30% due to performance degradation. The longest charge-discharge life cycle of large lithium-ion rechargeable batteries, such as automotive batteries, is currently between 2000-3000. However, Nippon Electric Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. believes that the life of the new positive electrode material even exceeds the above data. In the evaluation phase, a common carbon-based negative electrode is used in conjunction with the new material electrode.
Currently, the company is embarking on a new cathode material for automakers, electronic component manufacturers and power-related companies to evaluate the performance of new materials.
Boat Mooring Chain,Marine Anchor Chain,Cargo Ship Anchor Chain,Anchor And Anchor Chain
Jiangsu Zhongcan Marine Equipment Co.,Ltd. , https://www.anchorchainzc.com