Since the late 1990s, the Toyota Motor Corporation's operating scale has expanded significantly, placing higher demands on quality and cost control. Since the 21st century, Toyota has successively implemented two major innovative programs in cost control, which has achieved a high level of profitability in a certain period of time. However, under the financial crisis and Toyota recalls that began in the United States, The company lost for the first time in 70 years since its founding and has not recovered in the next two years.
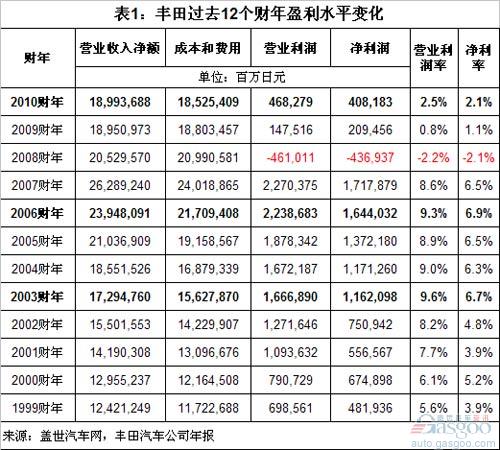
Toyota Motor Corporation has implemented a three-year cost-reduction plan since 2000: “CCC21 Plan†(Cost Competitiveness Construction Plan for the 21st Century), April 2002-2003. 3 The fiscal year of the month reached a high point of cost savings, which saved costs by 300 billion yen. In the following financial year, the company also achieved an operating profit margin of 9.6% and a net interest rate of 6.7%. Compared with fiscal year 1999, the company's operating profit margin and net profit margin were only 5.6% and 3.9%, respectively, and there was a big breakthrough. At the same time, the company’s operating income also increased from 12.4 trillion yen in fiscal 1999 to 17.3 trillion yen in fiscal year 2003.
In order to further reduce costs, more water was squeezed out of the dry towels. Since April 2005, the company has started implementing the “VI Plan†(value innovation plan). The company stated that the CCC21 plan is a project-based cost innovation plan, and the VI plan is a system-based cost innovation plan. An example of cost reduction under the VI plan is to reduce the thickness of rubber parts by about half while ensuring quality and performance, thus reducing the use of rubber, a rising price for raw materials, by 30%.
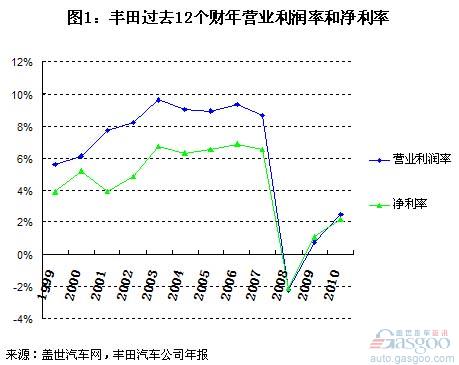
After the implementation of the VI plan, in fiscal year 2005-2007, although Toyota’s operating income rose to its highest peak in the fiscal year 2007 – 26.3 trillion yen, its operating profit rate remained at around 9%, the highest level (FY2006). It reached 9.3%, not exceeding the level of the 2003 fiscal year; while its net interest rate remained at around 6.6%, and the highest (also in fiscal 2006) reached 6.9%, setting a new record for at least 10 years.
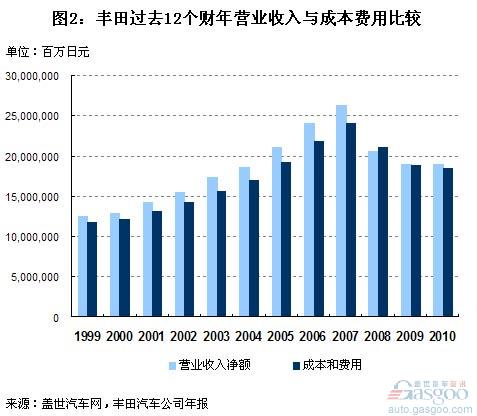
If time stops, Toyota's high-profit corporate image may not stand still. However, in 2008, the financial crisis that began in the United States suddenly turned Toyota, which had such a high level of profitability, into a loss-making ice cave. In fiscal year 2008, Toyota Motor Corporation’s operating revenue decreased by 21.9% year-on-year to 20.5 trillion yen, which was lower than the sum of costs and expenses (21.0 trillion yen). The company’s first loss in more than 70 years since its establishment, operating loss and net loss were respectively It reached 4610.1 billion yen and 436.94 billion yen. In the following two years, Toyota recovered from losses, but its operating revenue did not exceed 19 trillion yen. As of fiscal 2010, its operating margins and net margins have only risen to 2.5% and 2.1% respectively, not to their levels of more than ten years ago. At the same time, the large-scale recall of Toyota Motors in the world over the past two years has caused its quality to be discredited.
Toyota, a company that pays so much attention to reducing costs, has fallen into a situation of low profitability. Although there is no lack of financial crisis, Toyota's own problems are fundamental. These issues include (but are not limited to): over-reliance on the North American market, attention and investment in emerging markets such as China; over-centralized management does not give enough authority to decentralize regional markets; overemphasizes profits and reduces costs, and No new achievements have been made in quality assurance. On the contrary, in the case of rapid expansion, quality assurance has declined.
Note:
1. The fiscal year from April 2010 to March 2011 was known as the "FY2011 fiscal year" at Toyota Motor Corporation. However, to facilitate reading habits for Chinese readers and to unify with other Japanese car companies, we will call this in the article " "FY 2010", the title of other fiscal years and so on.
2. All data are taken from the consolidated financial statements prepared by Toyota Motor Corporation in accordance with US GAAP.
Hydraulic Cable Puller-tensioner
The hydraulic puller-tensioner can be used either as a puller or as a hydraulic tensioner in tension stringing operations. According to different models, it is possible to string from one or two or bundled conductors at the same time. The bull-wheel grooves consist of high resistance interchangeable nylon sectors or of wear-proof heat and chemically treated steel. The puller-tensioner is used for tension stretching and reverse pulling of double split conductors in flat, mountainous and hilly terrain. This equipment is suitable for replacing old conductor wire with a new one.
The main stander is made by customized rectangular steel tubes which are formed by one take art,to avoid any deformation which cause the mechanical parts. The bull-wheel grooves are made up of high resistance interchangeable nylon sectors. Hydraulic power pack to drive 1 drum stand with hydraulic motor. Apart from as a hydraulic cable tensioner, it could be used as puller by its pull back funciton. Working parameters of the machine,in cluding the length of stringing could be seen directly on digital meter counter. Hydraulic front stabiliser. Grounding connection point and temporay anchor point.
Hydraulic Cable Puller-Tensioner,Hydraulic Puller Tensioner,Puller-Tensioner,Stringing Hydraulic Puller-Tensioner
Taizhou Haoxin Electric Power Machine Co., Ltd. , https://www.hxstringingequipments.com